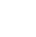Phyllodes Tumor is a tumor that develops in the breast. Hearing about breast tumors, the first thing that arises in one’s mind is tumor formation in the fatty tissue that makes up the volume of the breast. However, there are multiple tissues in our breast in addition to fatty tissues. However, Phyllodes Tumor appears in the connective tissues that hold the fatty tissues and glandular tissues (that produce milk) together.
What is a Phyllodes Tumor?
A phyllodes tumor is a rare type of breast tumor that develops in the connective tissue of the breast rather than the ducts or glands where most breast cancers originate. You may develop this tumor as benign (non-cancerous), borderline, or malignant (cancerous), depending on their behavior and risk of spreading or coming back after treatment.
Benign tumors are the most common type and are the least likely to spread or come back. Borderline tumors have some worrisome traits but aren’t fully cancerous. Malignant tumors are cancerous, grow quickly, and are more likely to spread or return after treatment.
These tumors start in the breast’s connective tissue, not in the ducts or glands where most breast cancers begin. Since they can look a lot like a common non-cancerous lump called fibroadenoma, doctors need to carefully study the tissue under a microscope to make the right diagnosis. You might want to know about the difference between tumors and cancer. Learn about oncology studies.
How Common are Phyllodes Tumors of the Breast?
Breast cancer is one of the most common cancers affecting females or people assigned female at birth, with a wide range of types and characteristics. While many breast tumors arise in the ducts or glands, a small fraction originates in the breast’s connective tissue, forming less common types such as phyllodes tumors.
Phyllodes tumors are rare fibroepithelial neoplasms, accounting for only 0.3% to 1% of all breast tumors. The World Health Organization classifies phyllodes tumors into three types: benign, borderline, and malignant. This classification depends on features like cell structure, how dense the tissue is, how fast cells are dividing, and if the edges look well-defined. We will describe the types in detail in a later section.
Types of Phyllodes Tumors
This tumor is categorized into three distinct types based on its behavior and growth patterns. If you have a phyllodes tumor, you may suffer from one of these conditions:
Benign Phyllodes Tumors
They are non-cancerous and account for the majority of cases. These tumors typically grow slowly and have a low risk of spreading or returning after treatment. They are often easier to treat due to their low recurrence potential.
Borderline Phyllodes Tumors
They fall between benign and malignant categories. While they show some signs of abnormal growth, they do not fully exhibit the characteristics of cancer. Borderline tumors have a moderate chance of growing or returning after treatment, so they require close monitoring.
Malignant Phyllodes Tumors
They are cancerous and makeup about 25% of all phyllodes cases. These tumors tend to grow quickly, often presenting as a fast-growing breast lump and have a higher risk of spreading to other parts of the body or recurring after treatment. Due to their aggressive nature, malignant types often need more intensive management.
These classifications are based on the behavior and growth pattern, breast cancer can also be classified based on their location. If the cancer stays at a location, it is primary, while if it relocates, it is called secondary breast cancer.
Phyllodes Tumor Symptoms – How Does it Feel Like having Phyllode Tumor?
Phyllodes tumor symptoms require an optimal check and distinguishing them from others. It usually feels like a hard, smooth lump in the breast. It’s typically well-defined and often grows quickly, sometimes reaching over 3 cm within a few weeks. As it enlarges, it can stretch the skin, making it appear shiny, translucent, or even sore. Interestingly, these tumors tend to appear more often in the left breast than in the right.
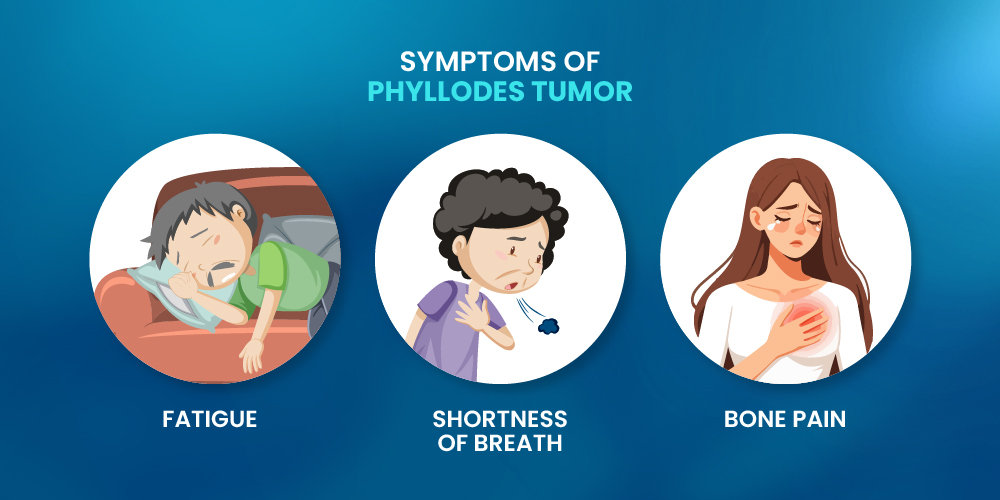
If the tumor is malignant, additional symptoms might develop, including:
- Fatigue
- Shortness of breath
- Bone pain
These symptoms could suggest that cancer has spread to the bones or lungs. If you notice any unusual breast changes, it’s important to consult a healthcare provider for a full evaluation of symptoms.
Causes of Phyllodes Tumor
If you are concerned about the cases, let us inform you, the causes can be multiple, either genetic or hormonal changes.
These tumors can develop at any age but are most common in middle-aged individuals. If you are suffering from Li-Fraumeni syndrome, a genetic disorder associated with a higher cancer risk, you may be more susceptible to this tumor. Some studies also mention a few family cases, such as those involving both a mother and daughter.
While the genetic risk factors for phyllodes tumor breast growth remain mostly unknown, researchers believe hormonal and growth factors may play a role. For instance, growth factors from the breast’s epithelium and higher levels of estrogen during pregnancy and lactation may encourage tumor growth. Endothelin-1, a substance that stimulates breast fibroblast growth, could also contribute. However, the precise role of these factors is not completely understood.
Read More: Understanding Pancoast Tumors
Diagnosis of Phyllodes Tumor
The diagnosis of phyllodes tumor breast requires a series of tests and screening tests.
They are often first detected as firm, painless lumps in the breast, though they may cause discomfort in some cases. These tumors tend to grow quickly, sometimes stretching the skin over the affected area.
To begin the diagnostic process, your healthcare provider may use imaging tests, such as mammograms or ultrasounds. It helps differentiate the tumor from other breast lumps. However, these imaging tests alone cannot confirm a phyllodes tumor breast, as they can resemble fibroadenomas.
To diagnose this type of tumor, doctors usually perform a core needle biopsy. This involves using a hollow needle, often guided by ultrasound, to take a small sample of the tumor for testing. If the results aren’t clear or the tumor looks suspicious, they might recommend an excisional biopsy, which means removing the whole tumor for a closer look. The biopsy will show if the tumor is benign, borderline, or malignant. If it’s malignant, more tests may be needed to see if it has spread to other parts of the body.
Phyllodes Tumor Treatment
Phyllodes tumor treatment usually involves surgery to remove the tumor completely. Even if a tumor is benign, healthcare providers recommend removing it to prevent future growth, discomfort, or the chance of it becoming malignant.
For a benign tumor, an excisional biopsy may be sufficient if it removes the entire growth for phyllodes tumor treatment. However, if the tumor is borderline or malignant, a wider margin of healthy tissue around the tumor must be removed to reduce recurrence risk.
If the tumor is malignant or bulky tumors, radiation therapy may be recommended after surgery, especially if there’s any uncertainty about the tumor’s complete removal. This approach reduces the chance of local recurrence. Additionally, follow-up care after surgery is essential, as this tumor can sometimes come back. Regular breast exams and imaging tests help ensure any recurrence is detected early.
The Importance of Clinical Trials for Breast Cancer
Breast cancer clinical trials are essential for advancing treatments and improving outcomes for those affected by both primary and secondary breast cancer. These trials help researchers discover new therapies, refine existing ones, and explore innovative options for patients at all stages of disease. Clinical trials can give you access to new treatments that might work better and have fewer side effects.
For individuals with metaplastic breast cancer, bone metastasis, clinical trials are especially valuable. They can provide you with an opportunity to explore treatments that target specific areas of metastatic disease, potentially offering better management and an improved quality of life. By joining these trials, patients get access to new treatments and help advance research that could benefit future generations with breast cancer.
Also Read: How to Prevent Brain Tumor – A Guide on Reducing Your Risk of Brain Tumor
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding and treating phyllodes tumors requires specialized care and a proper follow-up to manage the risk of recurrence. Surgical removal remains the primary treatment, with additional interventions like radiation therapy if the tumor is malignant.
Furthermore, for those affected by rare tumors like phyllodes or more common forms of breast cancer, participation in clinical research studies in Nebraska can offer access to potential treatments and innovative care approaches.
By joining these clinical trials, patients contribute to advancing medical knowledge. Additionally, you can gain potential benefits from potential therapies that could improve treatment outcomes and quality of life.