Bulky lymphoma is a condition that many people find challenging to understand due to its complex nature. More often, patients and their families ask, “What is bulky lymphoma?” This term refers to a form of lymphoma characterized by large tumor masses, typically measuring more than 10 centimeters. However, it can occur in both Hodgkin and non-Hodgkin lymphoma, making it a significant aspect of lymphoma diagnosis and treatment. Therefore, this article delves into the causes, stages, symptoms, and treatment of bulky lymphoma, with a special focus on advanced cases like stage 4b bulky lymphoma.
What Is Bulky Lymphoma?
Lymphoma is a type of cancer that originates in the lymphatic system, an integral part of the immune system. However, bulky disease is not a specific subtype but rather a term used to describe the size of the tumor. Therefore, the term “bulky” generally refers to tumors larger than 10 centimeters or those occupying a significant portion of the chest cavity.
Bulky masses are often seen in aggressive types of lymphoma, such as Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma (DLBCL) and Primary Mediastinal B-Cell Lymphoma. Additionally, these large lumps are most common in advanced stages, particularly in cases of stage 4b bulky lymphoma, which is characterized by widespread cancer and systemic symptoms.
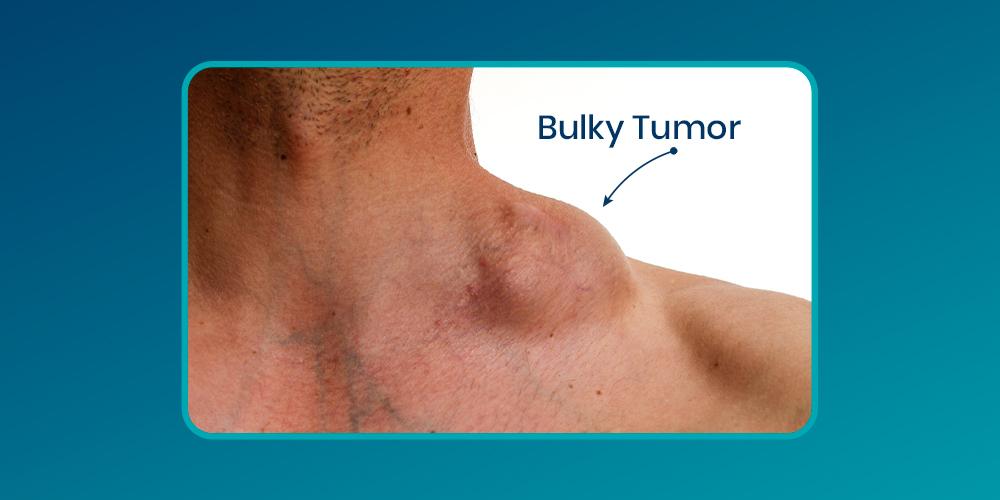
Types of Lymphoma Cancer That Can Be Bulky
Lymphoma is classified into two main categories: Hodgkin vs Non-Hodgkin lymphoma.
1. Hodgkin Lymphoma (HL):
Hodgkin Lymphoma is the type of lymphoma that includes Reed-Sternberg cells, making it easier to identify under a microscope.
2. Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma (NHL):
A broader category that includes various aggressive and indolent forms of lymphoma.
Bulky tumors are more commonly seen in the following types of lymphoma cancer:
Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma (DLBCL):
This aggressive form is one of the most common types of non-Hodgkin lymphoma.
Primary Mediastinal B-Cell Lymphoma:
A subtype of DLBCL that often presents with bulky tumors in the chest.
Early Stage Hodgkin Lymphoma:
Bulky disease can also occur in early stages, requiring tailored treatment plans.
Symptoms of Bulky Lymphoma
Moreover, bulky lymphoma is associated with symptoms that are both specific to the condition and general to lymphoma. Therefore, recognizing these symptoms early can lead to a quicker diagnosis and better outcomes.
Key symptoms include:
- Large lumps: However, visible or palpable masses in the neck, chest, armpits, or groin are common.
- Persistent fatigue and weakness.
- Fever and night sweats, which are part of the “B symptoms” often seen in lymphoma.
- Unexplained weight loss.
- Breathing difficulties or chest pain, especially if the bulky tumor is in the chest.
Additionally, patients may also experience symptoms commonly associated with other types of lymphoma, such as those seen in Symptoms of Follicular Lymphoma.
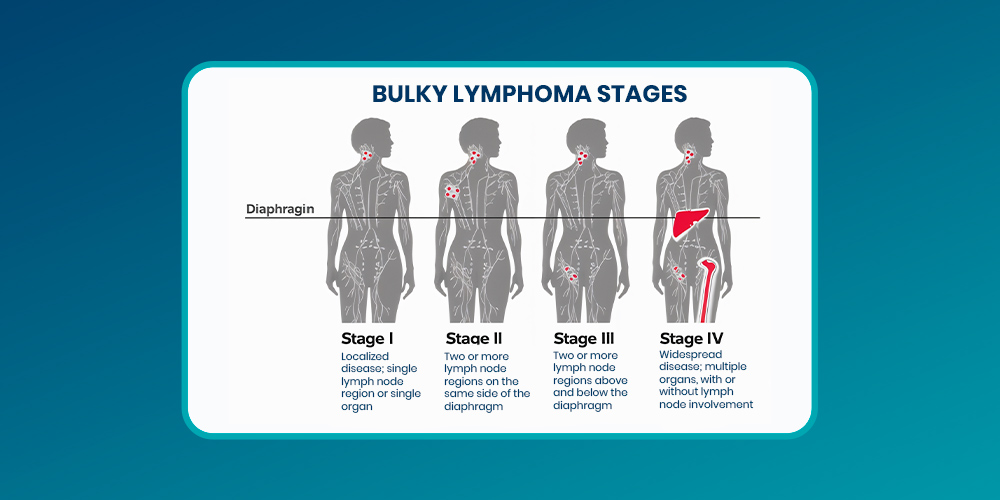
Stages of Lymphoma and Bulky Disease
The stages of lymphoma indicate how far the cancer has spread and help determine the best course of treatment.
1. Stage I:
Cancer is confined to one lymph node region or a single organ.
2. Stage II:
Involves two or more lymph node regions on the same side of the diaphragm.
3. Stage III:
Affects lymph nodes on both sides of the diaphragm.
4. Stage IV:
Cancer has spread to other organs, such as the liver, lungs, or bone marrow.
Nevertheless, bulky lymphoma can occur at any stage but is more commonly seen in stage 4b bulky lymphoma, where the disease is advanced and accompanied by systemic symptoms.
Diagnosis of Bulky Lymphoma
Accurate diagnosis is crucial for understanding what is bulky lymphoma and planning effective treatment. Nonetheless, several diagnostic tests are in place to identify the condition:
1. Imaging Tests:
CT scans, PET scans, and X-rays help determine the size and location of the tumor.
2. Biopsy:
A sample of the affected lymph node or tissue is examined under a microscope for confirmation.
3. Blood Tests:
These check for abnormalities in blood cell counts and organ function.
In advanced cases, patients may require additional tests to evaluate the extent of the disease.
Treatment for Bulky Lymphoma
Treatment for bulky lymphoma varies depending on the type and stage of the disease. Options include:
1. Chemotherapy:
The most common treatment, especially for advanced stages like stage 4b bulky lymphoma. Doctors also use combination regimens such as R-CHOP.
2. Radiation Therapy:
Used to shrink large lumps, particularly those in the chest cavity.
3. Immunotherapy:
Drugs like monoclonal antibodies help the immune system target and destroy cancer cells.
4. Stem Cell Transplant:
In cases where initial treatments fail, a stem cell transplant may be recommended.
Patients with conditions like Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma or Primary Mediastinal B-Cell Lymphoma can benefit from participation in Clinical Trials for Oncology, which offer access to innovative therapies.
Living with Bulky Lymphoma
Managing bulky lymphoma involves more than just medical treatment. However, patients may experience physical, emotional, and psychological challenges. Therefore, support from healthcare providers, family, and support groups is crucial for coping with the disease.
Additionally, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including proper nutrition and exercise, can also improve overall well-being during treatment.
Ongoing Research and Clinical Trials
Advancements in lymphoma research are paving the way for more effective treatments. Moreover, participation in clinical trials can provide patients with access to new therapies that are not yet widely available. For instance, studies focusing on Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma Clinical Trials and other aggressive lymphomas are exploring innovative approaches to treatment.
Similarly, conditions like Primary Mediastinal B-Cell Lymphoma and Symptoms of Follicular Lymphoma are being studied extensively, offering hope for improved outcomes.
Conclusion
Bulky lymphoma is a complex condition that poses unique challenges in diagnosis and treatment. Nonetheless, understanding what is bulky disease, recognizing its symptoms, and seeking timely medical care are crucial for effective management. Whether it’s early-stage Hodgkin lymphoma or advanced cases like stage 4b bulky lymphoma, personalized treatment plans and supportive care can make a significant difference.
For patients interested in exploring innovative therapies, participating in Clinical Trials for Oncology can be a valuable option. Therefore, to learn more about the latest advancements, consider consulting resources dedicated to conditions like Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma and Primary Mediastinal B-Cell Lymphoma.
However, with early detection, advanced treatment, and a strong support system, patients can face the challenges of bulky disease with confidence and hope.