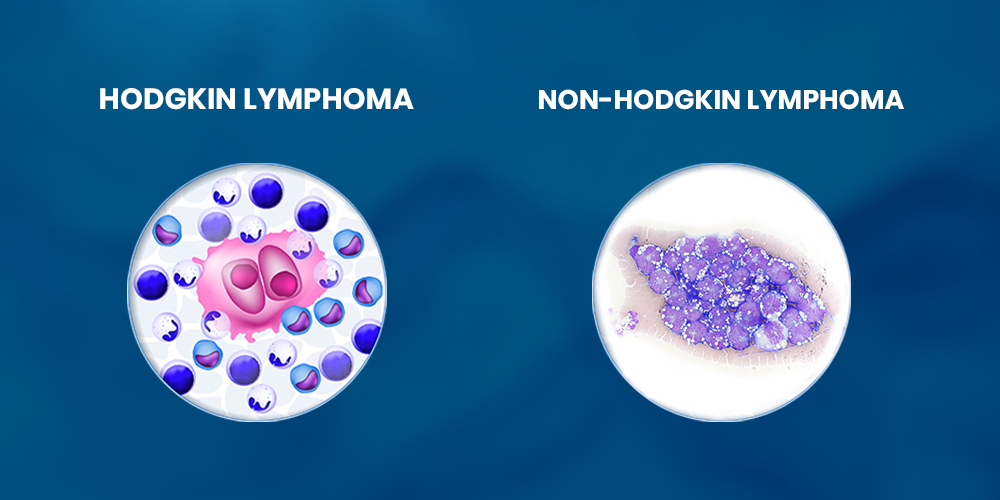
Hodgkin VS Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma: As much as their names coincide, the two possess some key differences. Although both are types of cancer that adversely affect the body’s lymphatic system, they appear differently under the microscope. Moreover, their attributes, treatments, and prognosis also vary. Their titles come from the name of the revolutionary researcher, Dr. Thomas Hodgkin, who documented the illness’ symptoms.
In this blog, we delve deeper into the difference between Hodgkin and non-Hodkin lymphoma.
The lymphatic system and development of lymphomas
To understand Hodgkin VS non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas completely, it is essential to grasp what a lymphoma is. Precisely, these are tumors that develop anywhere within the lymphatic system. It is the storehouse of white blood cells and forms the body’s defense mechanism. Since the lymphatic fluid travels across various regions of the body, the lymphomas can reach various destinations where the lymph tissues are found. For example, the lymph nodes, lymph vessels, spleen, thymus, bone marrow, tonsils, and adenoids.
What is Hodgkin’s lymphoma?
Hodgkin’s lymphoma is a rare condition that triggers abnormal cell multiplication in the lymphatic system. However, this type of lymphoma is characterized by the presence of specific Reed-Sternberg cells. These are large and possess multiple nuclei, allowing oncology researchers to identify them under a microscope. Eventually, these aberrant cells accumulate, promote tumor growth, and impair the body’s ability to battle infections.
What is non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma?
On the other hand, non-Hodgkin follicular lymphomas do not possess Reed-Sternberg cells. Instead, it can arise from either B-cells or T-cells, which are types of white blood cells. Although its target organs are the same as Hodgkin’s lymphoma, it is more diverse and has various subtypes. The diversity of this category makes the Hodgkin VS non-Hodgkin lymphoma comparison even more critical, as the behavior of non-Hodgkin lymphoma can vary widely depending on the subtype.
Additionally, some other types of follicular lymphoma are designated by the abnormal division of different B-lymphocytes such as centrocytes and centroblasts. Some examples include:
Follicular lymphoma of the duodenum
One type of cancer that appears in the gut or small intestines is called duodenal follicular lymphoma. This kind of lymphoma frequently presents itself early and grows slowly. It usually does not progress to a more aggressive form of lymphoma, nor does it metastasize to other parts of the body.
Childhood-onset follicular lymphoma
This particular kind of follicular lymphoma usually affects youngsters, but it can also strike adults. Men are more likely than women to get pediatric lymphoma. Swollen lymph nodes develop around the head and neck during this syndrome. Typically, it is detected in its early stages and is curable.
Hodgkin vs non-Hodgkin lymphoma: How to differentiate?
Apart from the key differences related to Reen-Sternberg’s cells, there are other critical distinguishing factors to consider. Primarily, though both conditions are rare, non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma is more prevalent than Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Moreover, the median age group getting non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma is 67 years, representing older people. Whereas Hodgkin’s lymphoma can also develop in young adults of around 39 years.
Additionally, the target body parts are another key identifier of Hodgkin’s VS non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. While Hodgkin’s lymphoma develops in the upper body; usually the neck, armpits, and chest, non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma may appear in any of the body’s lymph nodes. Also, it is easier to diagnose Hodgkin’s lymphoma due to its differential yet predictable way of progression.
Causes of Hodgkin and non-Hodgkin lymphoma
It is essential to understand the etiology of lymphomas to avoid, manage, and treat them in the future. Although the precise causes are still mostly unknown, oncology research studies have identified the following risk factors:
Genetic predisposition: The chance of getting a lymphoma may be influenced by family history.
Immune system suppression: HIV/AIDS and other illnesses that compromise immunity raise the risk. The Epstein-Barr virus also increases the chances of having these diseases.
Gender: Hodgkin VS non-Hodgkin lymphomas are more common in men than in women.
Environmental factors: The risk of both types may be increased by exposure to harmful chemicals or radiation.
Symptoms
Mostly, the symptoms of Hodgkin vs non-Hodgkin lymphoma are similar. However, patients of Hodgkin’s lymphoma report additional inflammatory symptoms. There have been reports of lymph node pain after consuming alcohol or having a hot bath. Other common signs of both conditions include:
- Swelling of the lymph nodes of the groin, neck, or armpits
- Elevated and unexplained fever
- Sweats at night
- Significant decrease in weight
- Severe itching
- Persistent feelings of exhaustion
Treatment of Hodgkin VS non-Hodgkin lymphoma
Usually, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, or a mix of the two are used to treat Hodgkin lymphoma. Its prognosis is often relatively good because it responds well to treatment. Early-stage Hodgkin lymphoma can have a five-year survival rate of nearly 80%, underscoring the significance of prompt treatment.
Meanwhile, in non-Hodgkin lymphoma, the stage and subtype of frequently influence how the disease is treated. Certain varieties can be treated with targeted medications or cautious waiting, while others could need severe chemotherapy. Non-Hodgkin lymphoma has a widely variable prognosis; certain subtypes respond well to treatment, while others may be more difficult to control.
Conclusion: Understanding Your Diagnosis
In conclusion, understanding the Hodgkin VS non-Hodgkin lymphoma debate is crucial for patients and their families. The key differences between these two types of lymphoma highlight the importance of accurate diagnosis and tailored treatment plans. If you’re wondering what is follicular lymphoma or need more information about various subtypes, resources are available to guide you through your options. Follicular Lymphoma Clinical Trials in Nebraska are an excellent opportunity to connect with those suffering from the same condition as you.
When facing Hodgkin vs non-Hodgkin lymphoma, knowledge is power. Stay informed, consult healthcare professionals, and actively participate in discussions about your health. By understanding your diagnosis, you can take proactive steps toward managing your condition effectively. For more resources and information, visit NHO Revive Research to stay updated on the latest research and treatment options. Additionally, Clinical Research Studies Near You in Nebraska can offer hope and new possibilities in treatment. Remember, every patient’s journey is unique, and there is support available for each step of the way. By educating ourselves on the difference between Hodgkin and non-Hodgkin lymphoma, we can better advocate for our health and well-being.