Richter transformation is a rare but serious condition where chronic leukemia turns into aggressive lymphoma. However, this shift worsens the disease, making treatment more challenging. Early detection is crucial, as Richter’s syndrome significantly impacts survival and treatment options.
Introduction: What is Richter Syndrome?
Richter’s syndrome is a rare but aggressive complication of chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). It occurs when leukemia transforms into a more aggressive type of lymphoma, such as diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) or Hodgkin lymphoma.
This transformation can happen suddenly, making treatment more difficult. However, patients often experience rapid tumor growth, worsening symptoms, and resistance to standard leukemia treatments. Therefore, understanding the causes of Richter transformation and its symptoms is essential for early diagnosis and better treatment outcomes.
In this blog, we will explore the causes of Richter’s syndrome, its symptoms, treatment options, and ongoing research. By the end, you’ll know what to look for and the available options for managing this condition.
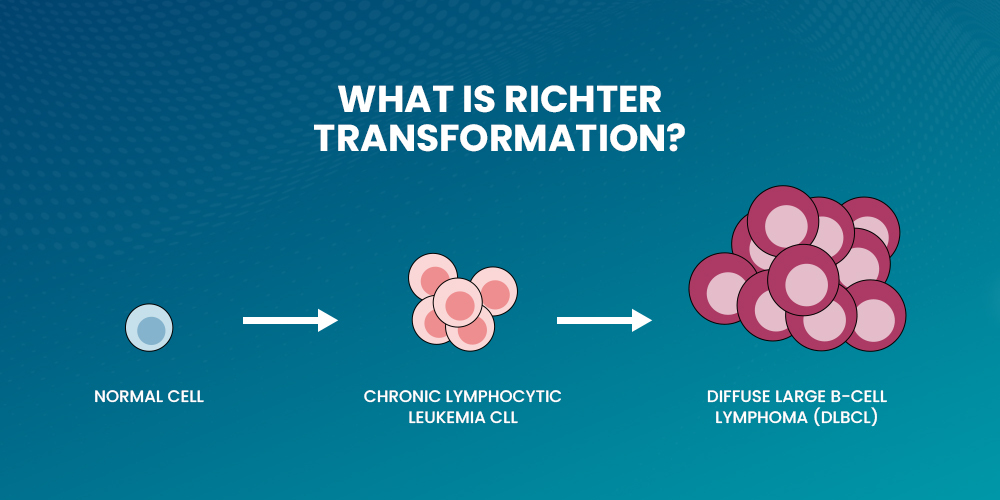
Understanding Richter Transformation: What Happens to the Body?
Richter transformation occurs when chronic leukemia changes into aggressive lymphoma. This shift leads to faster disease progression and worsens symptoms. Moreover, patients may notice sudden weight loss, fever and extreme fatigue.
Swollen lymph nodes often appear as an early warning sign. Additionally, these swollen nodes grow rapidly and feel harder than before. However, unlike typical leukemia, Richter transformation spreads quickly to organs like the liver and spleen.
Over time, cancer cells multiply at an uncontrollable rate. However, this leads to severe complications, including organ damage and increased resistance to treatment. Therefore, doctors must identify this transformation early to adjust treatment plans and improve outcomes.
What are the Causes of Richter Transformation?
Richter transformation can develop in patients with small lymphocytic lymphoma due to various factors. However, some cases occur without warning, while others follow a pattern of genetic changes.
Certain genetic mutations make leukemia cells more aggressive. Furthermore, these mutations allow abnormal cells to grow uncontrollably, increasing the risk of transformation. Doctors often check for specific mutations to predict this change.
Environmental factors may also contribute. However, long-term exposure to toxins, chronic infections, and a weakened immune system may increase the risk. Research continues to uncover why some patients develop Richter transformation while others do not.
Recognizing Richter’s Syndrome Symptoms: When to Be Concerned
Richter’s syndrome causes sudden and severe changes in leukemia symptoms. However, patients often feel extreme fatigue, night sweats, and unexplained weight loss. Fever and swollen lymph nodes that grow quickly are also common warning signs.
The difference between standard leukemia vs lymphoma symptoms is crucial. Leukemia usually causes gradual symptoms like anemia and frequent infections. In contrast, Richter transformation leads to rapid tumor growth, intense pain, and organ involvement.
Patients should seek medical attention if symptoms worsen quickly. Persistent high fever, severe swelling, or drastic weight loss may indicate transformation. Early diagnosis helps doctors adjust treatments before the disease spreads further.
How is Richter Syndrome Diagnosed?
Doctors use several tests to confirm Richter syndrome. However, blood tests detect abnormal cell changes, while imaging scans show enlarged lymph nodes or organ involvement. Therefore, these tools help track disease progression.
How Is Leukemia Diagnosed? plays a key role in identifying early changes. Bone marrow biopsies and flow cytometry help doctors analyze cancer cell behavior. Moreover, a sudden increase in aggressive cells may suggest Richter transformation.
To distinguish Richter syndrome from other lymphomas, doctors perform genetic tests and tissue biopsies. Additionally, these tests identify specific mutations linked to transformation. Early and accurate diagnosis allows for better treatment planning.
Treatment Options: What Can Be Done for Richter’s Syndrome?
Doctors use different approaches to treat Richter transformation. The treatment choice depends on the patient’s health and disease stage. Some options focus on controlling symptoms, while others aim for long-term remission.
Chemotherapy remains a common treatment. Strong drug combinations help shrink aggressive lymphoma cells. However, not all patients respond well, and side effects can be severe.
Targeted therapies provide a more precise approach. These treatments attack cancer cells while sparing healthy ones. Some drugs block specific proteins that fuel tumor growth. Others help the immune system fight cancer.
Clinical trials offer new possibilities. Many trials explore treatments for Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma, which shares similarities with Richter syndrome. Patients who join these studies may access promising therapies before they become widely available.
Early treatment decisions impact survival. Doctors may suggest stem cell transplants if other options fail. This procedure replaces damaged cells with healthy ones, increasing the chances of remission.
The Role of Clinical Trials in Richter Syndrome Treatment
Clinical trials of Follicular Lymphoma may offer hope for Richter syndrome patients. Some trials test new drugs, while others combine existing treatments in unique ways.
New treatments for Richter transformation are essential. Standard therapies often have limited success, and patients need better options. Clinical trials help researchers find safer and more effective ways to manage the disease.
Patients should discuss trial opportunities with their doctors. Joining a study could provide access to cutting-edge therapies and improve future treatment strategies.
Prognosis: What Does the Future Hold?
Survival rates for Richter syndrome vary. Many factors influence outcomes, including patient age, overall health and treatment response. Early diagnosis and aggressive treatment can improve chances of survival.
Genetic changes play a key role. The presence of the Philadelphia Chromosome may affect treatment success. Some mutations make cancer cells more resistant to therapy, while others help doctors choose better treatment plans.
Treatment advancements continue to improve survival. New therapies, such as targeted drugs and immunotherapy, offer hope for better outcomes. Patients should discuss all available options with their healthcare team.
Conclusion: What’s Next for Richter Syndrome Patients?
Richter syndrome remains a serious condition, but treatment options are expanding. Early diagnosis and personalized care improve the chances of managing the disease.
Patients should explore every possibility. Research on T-Cell Lymphoma may lead to new therapies that could benefit Richter syndrome patients. Consulting a specialist and considering clinical trials can open doors to better treatment choices.