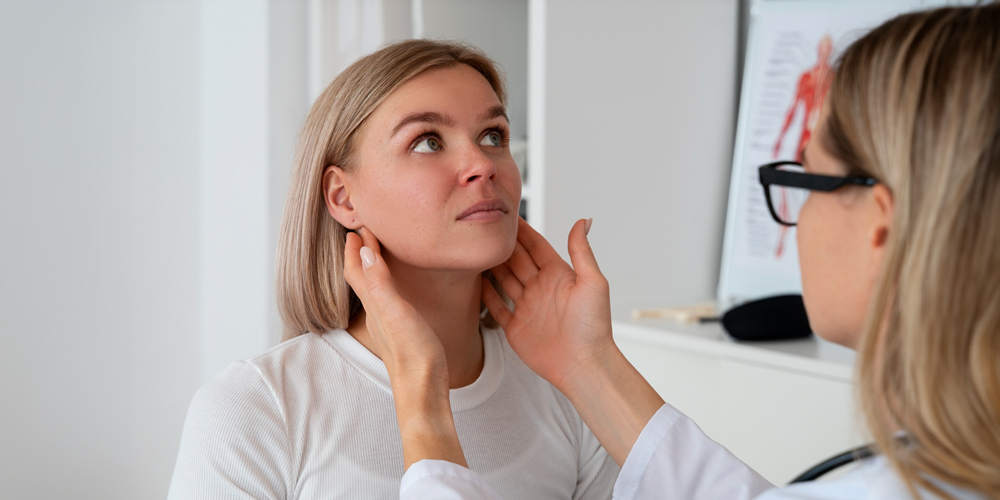
It affects the body by causing the lymph nodes to become enlarged. This, in turn, leads to symptoms like swelling and discomfort, and may also affect nearby organs. Moreover, the abnormal cells can interfere with normal immune system function, making the body less able to fight infections and other diseases.
Symptoms of Follicular Lymphoma
Common Symptoms:
- Swollen Lymph Nodes: Enlarged lymph nodes are often the most noticeable symptom. They can appear as lumps under the skin, usually in the neck, armpits, or groin. Moreover, you can easily feel these swollen nodes during a physical examination, and they can cause significant discomfort.
- Fatigue: Persistent and unexplained tiredness that doesn’t improve with rest can become a significant issue. Furthermore, this fatigue often interferes with daily activities and overall quality of life, making it difficult for individuals to maintain their usual routines.
- Unexplained Weight Loss: Significant weight loss without changes in diet or exercise often signals increased energy expenditure due to cancer. Additionally, this symptom can be a result of the body working harder to combat the disease.
- Night Sweats: Excessive sweating during the night that soaks through bedclothes and sheets is another common symptom. In addition, this can be accompanied by chills, further disrupting sleep and comfort.
- Fever: Persistent or intermittent fever without a clear cause can vary in intensity. Often, this fever may be low-grade or high and may not respond to standard treatments, signaling an ongoing issue.
Less Common Symptoms:
- Abdominal Pain or Bloating: Discomfort or swelling in the abdomen may result from enlarged lymph nodes or other related issues. Moreover, this can lead to additional gastrointestinal symptoms that affect daily life.
- Itchy Skin: Unexplained itching, which may be generalized or localized, can occur due to changes in the skin or underlying disease effects. Furthermore, this symptom may be a result of the body’s response to the lymphoma or related treatments.
Symptoms can differ based on the stage of the disease, individual health conditions, and the extent of lymph node involvement. For instance, some people might experience more pronounced symptoms, while others may have subtle or few symptoms.
Read More: Exploring Primary Mediastinal B-Cell Lymphoma: Key Facts and Insights
What Causes Follicular Lymphoma
Causes and Risk Factors
Some common follicular lymphoma causes and risk factors include:
- Genetic Predispositions: A family history of lymphomas or related cancers can increase risk. Additionally, specific gene mutations may also play a role.
- Environmental Factors: Exposure to certain chemicals, such as pesticides or industrial pollutants, may raise the likelihood of developing follicular lymphoma cancer.
- Possible Links to Autoimmune Diseases: Moreover, the immune system’s irregularities might contribute to lymphoma development.
- Age and Gender Influences: It commonly affects adults, especially those over 60. It is slightly more common in men than in women.
- Other Risk Factors: Past exposure to radiation or certain infections might also heighten the risk. Furthermore, a weakened immune system due to other health issues can be a contributing factor.
Diagnosis of Follicular Lymphoma
Common Diagnostic Tests:
- Physical Examination: A doctor checks for swollen lymph nodes and other physical signs of lymphoma. They may also inquire about symptoms and medical history.
- Blood Tests: These tests help identify abnormalities in blood cell counts and detect specific markers that may indicate lymphoma.
- Imaging Tests (CT Scans, PET Scans): CT scans provide detailed images of the lymph nodes and other organs, while PET scans detect areas of abnormal activity, helping to locate cancer spread.
- Biopsy Procedures: A biopsy involves removing a sample of lymph node tissue for microscopic examination. This helps confirm the presence of cancer cells and determine the lymphoma type.
- Importance of Early Diagnosis: Early detection improves treatment effectiveness and can enhance prognosis. Furthermore, it allows for timely intervention and potentially better outcomes.
Stages of Follicular Lymphoma
Healthcare providers determine the stage of follicular lymphoma to guide treatment decisions.
- Stage I: The cancer is present in one or more lymph nodes but is confined to a single area. This stage accounts for approximately 25% of follicular lymphoma diagnoses.
- Stage II: The cancer has spread to lymph nodes either above or below the diaphragm but remains limited to one side of the diaphragm. About 15% of cases are diagnosed at this stage.
- Stage III: The cancer is found in lymph nodes on both sides of the diaphragm. This stage represents around 26% of diagnoses.
- Stage IV: The cancer has extended beyond the lymph nodes to other areas, such as the bone marrow or various organs. Healthcare providers diagnose about 27% of cases at this advanced stage.
Treatments for Follicular Lymphoma
Treatment varies based on the stage, grade, and individual health factors. Consequently, the main goal is to manage symptoms and control cancer growth.
- Watchful Waiting: Also known as active surveillance, this approach involves regular monitoring without immediate treatment. Typically, it is used for patients with early-stage, slow-growing lymphoma who are not experiencing significant symptoms.
- Chemotherapy: In this treatment, drugs are used to kill or stop the growth of cancer cells. This can be administered either orally or through intravenous infusion. It is usually employed for more advanced stages or aggressive cases.
- Radiation Therapy: Here, high-energy radiation targets and destroys cancer cells in specific areas. Often, it is used for localized disease or to alleviate symptoms from enlarged lymph nodes.
- Targeted Therapy: This approach uses drugs that specifically target cancer cells or their environment, thereby minimizing damage to healthy cells. It can be given alone or in combination with other treatments.
- Immunotherapy: This treatment aims to boost or modify the body’s immune system to better recognize and attack cancer cells. It includes monoclonal antibodies and other immune system enhancers.
- Emerging Treatments and Clinical Trials: New therapies and combinations are continually being researched. Therefore, clinical trials offer access to innovative treatments that may not yet be widely available.
- Managing Side Effects of Treatment: Side effects vary depending on the treatment used. Common side effects are nausea, fatigue, hair loss, and a higher risk of infections. Fortunately, healthcare providers offer supportive care and medications to help manage these effects and improve the quality of life during treatment.
Follicular Lymphoma Clinical Trials
Follicular lymphoma clinical trials in Nebraska offer patients the chance to participate in groundbreaking research and access new treatment options. These trials frequently investigate innovative therapies, drug combinations, and advanced approaches aimed at improving patient outcomes and managing side effects. By joining a clinical trial, patients can benefit from cutting-edge treatments not yet widely available and receive expert care from leading professionals. Local cancer centers and research institutions often conduct these trials, providing valuable opportunities to advance the fight against follicular lymphoma while receiving personalized treatment.
Also Read: Understanding Bulky Lymphoma Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Conclusion:
In conclusion, follicular lymphoma presents various symptoms and treatment options, ranging from watchful waiting to advanced therapies like chemotherapy, radiation, and immunotherapy. For those seeking the latest advancements in treatment, clinical trials for oncology provide invaluable opportunities. Participating in these trials can offer access to cutting-edge therapies and personalized care not yet available to the public. By joining these trials, patients not only contribute to groundbreaking research but also benefit from innovative treatments that could significantly improve their outcomes.