When it comes to cancer, some types are more dangerous than others. But when it comes to blood cancer, how do you determine which is the most dangerous?
Blood cancers, unlike other types of cancer, don’t form solid tumors. Instead, they affect the blood, bone marrow, or lymphatic system, making them more challenging to treat and detect early.
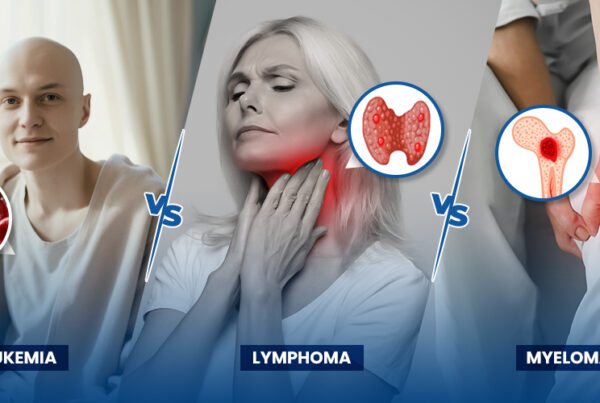
In this blog, we’ll overview the three main types of blood cancer—leukemia, lymphoma, and myeloma and find out which one is considered the most dangerous.
What is Blood Cancer?
Blood cancer, also known as hematologic cancer, affects the blood, bone marrow, or lymphatic system. Unlike solid tumors, blood cancers spread throughout the body quickly and can interfere with the production of blood cells, weakening the body’s immune system and overall function.
There are three main types of blood cancer, and understanding the differences between leukemia, lymphoma and myeloma is essential for diagnosis and treatment.
- Leukemia: This cancer affects the bone marrow and blood, resulting in abnormal production of white blood cells. It can spread quickly and is often aggressive.
- Lymphoma: This type of blood cancer affects the lymphatic system, where immune cells are produced. There are two main types: Hodgkin lymphoma and non-Hodgkin lymphoma.
- Myeloma: This affects the plasma cells, a type of white blood cell responsible for fighting infections. Myeloma weakens the bones and can lead to kidney problems.
What makes blood cancer so dangerous is its ability to spread throughout the bloodstream or lymphatic system, making it difficult to contain and treat. The rapid progression of these cancers is why early detection is crucial.
Which Type of Blood Cancer is Most Dangerous?
While all blood cancers are serious, leukemia—especially acute leukemia—is often considered the most dangerous due to its rapid progression.
It can overwhelm the body’s immune system in a short period, making it harder to treat and increasing the risk of complications.
Lymphoma, specifically non-Hodgkin lymphoma, is another dangerous type. The aggressive nature of certain subtypes like T-cell lymphoma makes it harder to treat and increases its fatal potential. Non-Hodgkin lymphoma has a high risk of spreading to other parts of the body, which complicates treatment further.
Myeloma, though progressing more slowly than leukemia and lymphoma, can still be fatal, especially if diagnosed at an advanced stage. The disease damages bones and organs, which leads to significant physical complications. It’s often harder to treat in older patients, as they may not be candidates for aggressive therapies like stem cell transplants.
Ultimately, the “most dangerous” blood cancer depends on the individual case, including the type, stage, and overall health of the patient. However, leukemia is often considered the most aggressive, followed by non-Hodgkin lymphoma and myeloma.
How Serious is Blood Cancer?
Blood cancer is one of the most serious types of cancer due to its ability to spread quickly and affect the body’s vital systems. Early detection is crucial, as untreated blood cancer can lead to severe complications, including organ failure, infections, and in some cases, death.
Challenges in Diagnosis:
Blood cancers don’t always present with obvious symptoms in the early stages. Patients may experience general symptoms like fatigue, fever, and weight loss, but these signs are often mistaken for other illnesses. Because blood cancers can spread so quickly, the delay in diagnosis can worsen the prognosis.
Read More: How Is Leukemia Diagnosed?
Treatment Challenges:
Treating blood cancer is complex. Chemotherapy, radiation therapy, stem cell transplants, and targeted therapies are commonly used, but they come with significant side effects and complications. Blood cancers also have a tendency to relapse, making long-term treatment plans necessary.
Also Read: Immunotherapy vs Chemotherapy: Understanding the Difference in Cancer Treatment
Survival Rates:
The survival rate of blood cancer varies depending on the type and stage of cancer. Acute leukemia has one of the lowest survival rates, but with early intervention, survival chances improve dramatically.
Non-Hodgkin lymphoma also has a relatively low survival rate for advanced stages, but certain types, especially those caught early, have a good prognosis. Myeloma’s survival rate has improved with new treatments, but it remains a serious disease.
Blood cancer is undeniably serious, but ongoing advancements in treatment are giving patients hope and improving survival rates.
Risk Factors of Blood Cancer
What are the risk factors for blood cancer? Understanding these factors can help with early detection and prevention.
- Genetics: If you have a family history of blood cancer, your risk may be higher.
- Age: Blood cancers are more common in older adults, particularly leukemia and myeloma.
- Environmental Factors: Exposure to certain chemicals or radiation, such as from working with toxic substances or undergoing radiation therapy, increases the risk.
- Previous Medical Conditions: Conditions like autoimmune disorders or previous cancers can increase the likelihood of developing blood cancers.
Leukemia risk factors include certain genetic disorders, smoking, and previous exposure to cancer treatments.
Myeloma is more common in individuals with weakened immune systems, while lymphoma risk increases with a weakened immune system, such as in patients with HIV.
Understanding these risk factors can help with early detection, improving treatment outcomes and overall survival rates.
Latest Research and Clinical Trials in Blood Cancer
Ongoing oncology research is making significant strides in blood cancer treatment. From new medications to targeted therapies, research is focused on improving survival rates and quality of life for blood cancer patients.
Innovations in Treatment:
New immunotherapies and gene therapies are showing promise in treating aggressive blood cancers like leukemia and lymphoma. These treatments specifically target cancer cells, sparing healthy cells and reducing side effects.
Clinical Trials:
Participating in oncology clinical trials can give patients access to cutting-edge treatments that are not yet widely available. Clinical trials in places like Nebraska have even seen highest paid clinical trials focused on blood cancer research, providing both hope and financial support for patients.
The future of blood cancer treatment looks promising, with research pushing the boundaries of what’s possible and improving the prognosis for many patients.
Read More: Leukemia vs Lymphoma: Understanding the Differences, Causes, and Treatments
Conclusion
To recap, blood cancers—leukemia, lymphoma, and myeloma—each present significant challenges, but acute leukemia is often considered the most dangerous due to its aggressive nature.
Understanding the risks, survival rates, and the latest advancements in research is essential for early detection and effective treatment.
Key Takeaways:
- Blood cancer spreads quickly and can affect the entire body, making it difficult to treat.
- Leukemia, particularly acute leukemia, is the most aggressive form.
- Ongoing research and clinical trials offer hope for improved treatments and survival rates.
If you or a loved one are at risk or experiencing symptoms, it’s important to seek medical advice for early diagnosis and explore clinical trial options to access innovative treatments. Stay informed and take action today.