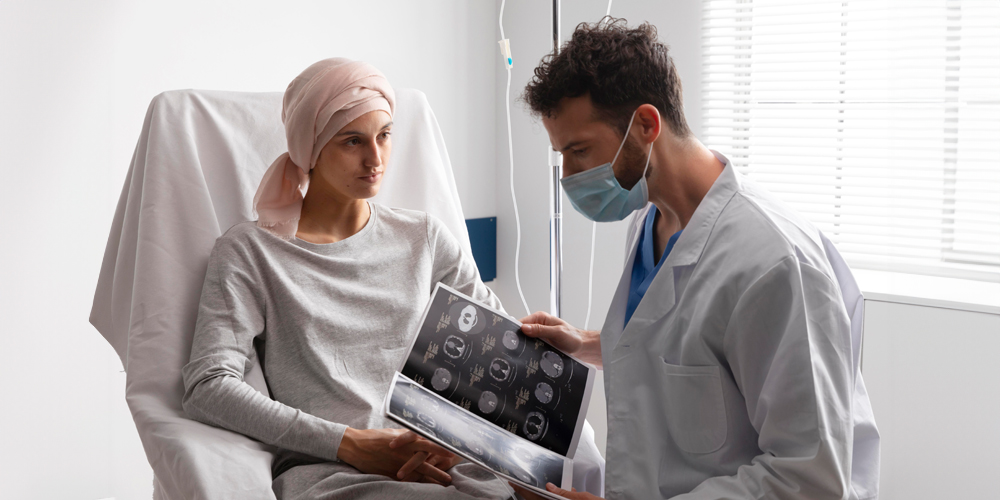
Recently, medical research has been of great service to the healthcare sector. It has drastically improved the modes of disease management, diagnosis, prevention, and treatment. According to a recent report, people are actively enrolling in more than 20,000 clinical trials in the USA. In this blog, we will outline the basics of oncology research and how it benefits the cancer society.
What is oncology research?
To be precise, if we break the term down into smaller chunks, ‘onco’ means tumor, and ‘logy’ means studies. In other words, oncology is a branch of medicine that deals with cancer-causing tumors. Oncology research studies investigate everything related to cancer intricately to come up with modern and effective therapy options. In oncology clinical trial phases, cancer patients and survivors share their journey with the researchers to foster social and medical welfare.
Oncology clinical trial phases
Before becoming the pioneer of the medical market, a prospect treatment module goes through in several steps of oncology research. However, it is only eligible to enter the next trial phase once it is proven successful in the first one.
- Phase 0 – Preliminary Assessment of the New Drug – 15 to 30 people
Firstly, specialists perform a preliminary examination of a new drug and its potential effects. Further, they may investigate whether the drug can effectively reach the tumor and how cancer cells respond to it. Moreover, small quantities of the medication are administered to a limited number of individuals to assess the human body’s reaction. - Phase I – Evaluating Treatment Viability – approximately 100 people
Secondly, researchers assess whether the treatment achieves its intended purpose. Also, they evaluate the safety of the treatment for future applications. Hence, this phase of oncology research is crucial for determining if the treatment should progress to subsequent stages. - Phase II – Assessing Treatment Efficacy – 100 to 1000 people
Thirdly, the treatment’s effects, side effects, and overall efficacy are thoroughly examined. More importantly, researchers may focus on determining whether the treatment is advantageous for specific types or stages of cancer. - Phase III – Comparative Effectiveness Evaluation
Next, this stage aims to ascertain whether the treatment offers advantages over existing standard treatment options. After that, they compare the new treatment with the most effective current therapies and assess accordingly. - Phase IV – Long-Term Treatment Monitoring
Finally, even after a treatment successfully completes all trial phases, further investigation is warranted over an extended period. Phase IV trials allow researchers to monitor the long-term effects and outcomes of the new treatment. With this, the potential treatment of oncology research either stays in the market or gets labelled inefficient.
The protocols of a clinical trial
The essence of a successful clinical trial rests in its compliance with industrial and ethical standards. Following are some measures that reliable clinical trials for oncology research must ensure compliance with:
- Clinical trial experts only test the most promising drugs and treatments on participants
- Taking informed consent with every single participant of the research. Specifically, the researchers must brief the subjects about all the procedures which will be part of the research.
- Ensuring an equal share of the advantages and loopholes for every participant
- Conducting pre-clinical research and complying with regulatory standards
- Getting a permission letter from FDA (US Food and Drug Administration) and getting the research reviewed by IRB (International Review Board)
The resourcefulness of oncology research
With respect to their adherence with technological advancements, oncology research studies are massively aiding the healthcare sector. Mentioned below, is a brief overview of the remarkable benefits of cancer clinical trials:
- Most importantly, the best innovative cancer therapies are first introduced to clinical trial participants.
- Investigators give more attention to patients in a research trial than regular patients. Every single symptom or reaction is closely monitored, enabling proficient treatment.
- Research trials grant cancer patients and survivors a chance to play their part in human welfare.
- Additionally, these trials also give the participants an opportunity to participate in scientific advancements.
- They help the doctors and scientists to design, test, and introduce extremely efficient drugs and treatments in the market.
- All treatments are thoroughly tested to be safe and effective.
- Often, oncology research offers a more economical alternative compared to conventional, costly cancer therapies and lengthy treatment processes.
Types of oncology research:
Basic research:
First and foremost, this research specifically focuses on the cellular and molecular transformation inside the body. Furthermore, it can be pre-clinical or simple lab research.
Translational research:
Next, this type of research bridges the gap between observational studies and clinical trials. More precisely, it puts the bookish work into real-life practice.
Clinical research:
Meanwhile, during clinical research, the researchers collect and analyze the patient’s data. Also, they make decisions based on it. For example, what treatments are applicable in the current scenario.
Epidemiological research:
In this research, scientists study a group of people from different backgrounds to unravel the causes, effects, patterns, and risks of cancer.
Questions you can ask a clinical trial representative:
- What are the benefits and risks of this trial?
- How long will the trial go on for?
- What kind of tests or procedures will be performed?
- What are the potential treatment options?
- Who will be in charge?
- What are the side-effects?
- Will my daily life be affected?
- Is the treatment invasive?
- How is customer service maintained?
Read more: Benefits of Clinical Research, Its Types, and Scope in Cancer Care
Conclusion:
Oncology research is saving the lives of many cancer patients across the globe. Together with that, it is protecting people from getting cancer anew. During these trials, scientists and medical experts work in collaboration to learn more about cancer. This helps them handle and treat cancer patients more effectively.
Additionally, there are several different types of cancer trials. Either they can be therapeutic or non-therapeutic. To clarify, therapeutic cancer trials are interested in the treatment of cancer. Whereas the non-therapeutic ones are more inclined towards screening, prevention, and supportive care.
In conclusion, clinical trials are a bright opportunity to escalate scientific advancements and do something beneficial for society. All participants are subject to informed consent when taking part in a cancer trial. As per an Antidote survey, 95% of the medical volunteers were interested in taking part in another trial.